User Guide
Project BUDDY is a Teacher’s Contact Management Application supported by CLI text input commands. Teachers can enter contact information for a swift search and retrieve desired contact information within a few keystrokes. The application provides an all-in-one display of the contacts related information and their details are presented in a beautiful scrolling view.
- Table of Contents
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
projectbuddy.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your Project BUDDY.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The GUI similar to the below should appear in a few seconds. Note how the app contains some sample data.
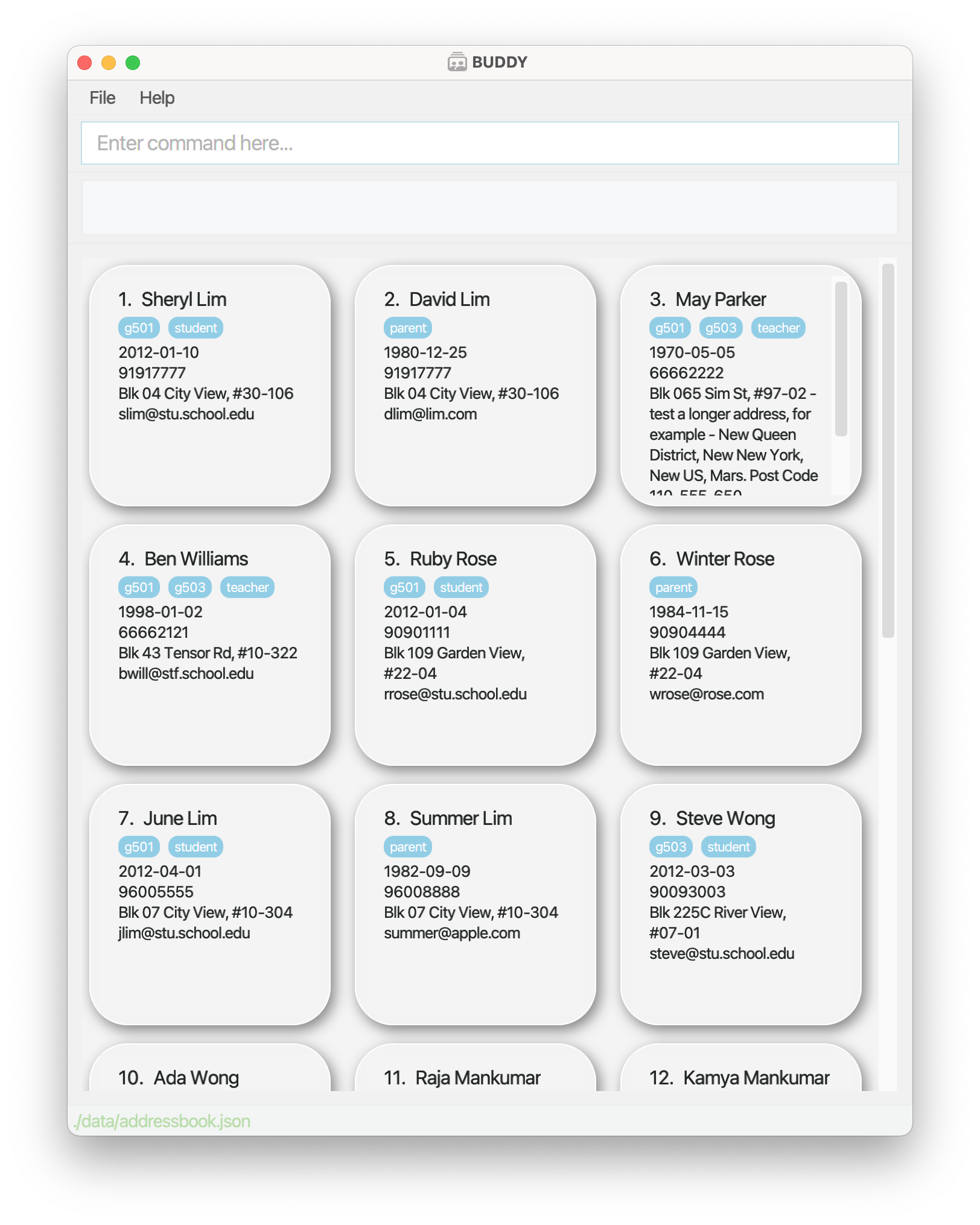
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will open the help window.
Some example commands you can try:-
list: Lists all contacts. -
addn/John Doe b/2020-01-01 p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01: Adds a contact namedJohn Doeto the Address Book. -
delete3: Deletes the 3rd contact shown in the current list. -
clear: Deletes all contacts. -
exit: Exits the app.
-
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Command corresponding to Feature
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
- Record people’s name, birthday, phone number, email and address: Format: add n/NAME b/BIRTHDAY p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS Example: add n/Duke b/2020-01-01 p/98001234 e/duke@gmail.com a/Duke street, block 1, #05-01
Viewing help : help
Shows a message explaining how to access the help page.
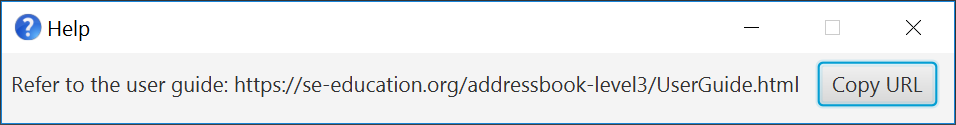
Format: help
Adding a contact: add
Create a new contact with info such as name, hp, email, address and optional number of tags.
Format: add n/NAME b/BIRTHDAY p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
Examples:
add n/Nana Park b/2000-01-01 p/9666 4222 e/nana@example.com a/620 Bedok Rd, 470620 t/student t/G5-C02
Editing a contact: edit
Edit an existing contact with info such as name, hp, email, address and optional number of tags.
Format: edit SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
Examples:
edit 1 n/John p/9001 4232 e/john@example.com a/621 Bedok Rd, 470623 t/colleague t/Math-department
Batch editing contacts: edit -batch
Edit existing contacts with info such as hp, email, address and optional number of tags.
Format: edit -batch SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT,SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
- SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT must be a positive integer.
- Cannot batch edit the name fields of the contacts.
Examples:
edit 1,2,3 p/9001 4232 t/Engineering-department
Delete a contact: delete
Format: delete SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT
- SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT refers to the numbering of the contact in the list.
- SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT must be a positive integer.
Example:
delete 2
View a list of contacts: list
Format: list
- All contacts’ name, phone number, email and address will be displayed.
Example:
list
Search contact by name: find
Format: find NAME
- NAME is case-insensitive. I.e.
find DUKEwill returnDuke’s contact. - NAME has to be a full word. I.e.
find DUKwill not returnDuke’s contact. - If NAME consists of two words, the sequence of words will not affect the search result. I.e.
find Duke Johnwill return bothJohn Duke’s andDuke John’s contacts. - Contacts matching either one of the NAME will be returned. I.e.
find Duke Johnwill return bothDuke MarkandCharles Duke’s contacts.
Example:
find Duke
Undo the previous command: undo
Format: undo
- The previous contact list will be recovered.
- Does not support command
rename
Example:
undo
Copy a contacts: copy
Format: copy SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT
- SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT refers to the numbering of the contact in the list.
- SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT must be a positive integer.
- A string of text of the contact details will be copied to clipboard.
- User can paste (CMD/CTL v) the details to a text field.
Example:
copy 1
Search contact by tag: filter
Format: filter TAG
- TAG is case-insensitive. I.e.
filter G501will returng501’s contact. - TAG has to be a full word. I.e.
filter G50will not returng501’s contact. - Contacts matching either one of the TAG returning a combined result set, the sequence of words will not affect the search result. I.e.
filter g501 g502will return bothg501’s andg502’s contacts.
Example:
filter g501
Search contact by name: rename
Format: rename TAG t/TAG
- To rename TAG for all contacts with TAG specified.
- TAG has to be a full word matching existing tag in the records.
- TAG is the existing tag that needs to be renamed.
- t/TAG is the tag to be renamed into.
- For TAG to be renamed into multiple TAG, you may do do by adding more parameter. I.e.
rename g501 t/graduated t/NUSwill remove all contact with existing ‘g501’ tag and add on new tag ‘graduated’ and ‘NUS’.
Example:
rename g501 t/graduated t/NUS
Remove tag from all contact: rename TAG t/
Format: rename TAG t/
- TAG is case-sensitive. I.e.
rename student t/will removestudenttag from all contact. - TAG has to be a full word. I.e.
find G50will not remove tagg501.
Example:
rename student t/
Search contact by birthday month: bday MONTH
Format: bday MONTH
- MONTH has to be within 1 to 12. I.e.
bday 1will return contact with birthday month of January. - Contacts matching either one of the month returning a combined result set, the sequence of words will not affect the search result. I.e.
bday 1 2will return all contact with birthday month in either January or February.
Example:
bday 1
Create relation among persons: relate
Relate multiple persons to someone
Format: relate TO_SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT <- FROM_SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT1 FROM_SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT2 ...
- The
relatecommand has a 1 to n relationship - TO_SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT on the left hand side of
<-is the target whom persons going to relate to - FROM_SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACTi on the right hand side of
<-is the group to relate to the target one by one - Relation is mutual. So A related to B, B also related to A automatically
Example:
relate 2 <- 1 4 5
Recommended usage:
- you could first
filterby tag like a class no.g503, then userelateto relate from all the students to a teacher in that class one at a time. - the SEQ_No_OF_CONTACT refers to the index no. of current displayed list, you could go back to the all contact list using
list.Show everyone related to a particular person
Format:
relate SEQ_NO_OF_CONTACT - When there is no
<-action symbol used,relateacts like a listing command that displays the person and whose every related persons
Example:
relate 2
So far, relate command does not support undo or deletion in v1.4, which could be considered for future updates.
Exit the program:
Format: exit
- The contact list will not be deleted after exiting.
Example:
exit
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous AddressBook home folder.
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Add |
add n/NAME b/BIRTHDAY p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]… e.g. add n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend t/colleague
|
| Edit |
edit INDEX n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]… e.g. edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.com a/111, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/student
|
| Batch edit |
edit -batch INDEX,INDEX n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]… e.g. edit -batch 1,2,3 p/92234567 e/johndoe@gmail.com
|
| Bday |
bday MONTH e.g. bday 12
|
| Delete |
delete INDEX e.g. delete 2
|
| List | list |
| Filter |
filter TAG e.g. filter student
|
| Find |
find NAME e.g. find steve
|
| Rename |
rename TAG t/TAG e.g. rename student t/graduated t/NUS
|
| Remove tag |
rename TAG t/ e.g. rename student t/
|
| Undo | undo |
| Copy |
Copy INDEX e.g. copy 1
|
| Relate |
relate INDEX_TO <- INDEX1 INDEX2 INDEX3 ... e.g. relate 2 <- 1 4 5 relate INDEX e.g. relate 2
|
| Exit | exit |